Check If Selinux Is Enabled

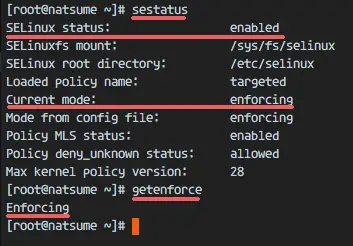
Aug 14, 2018 - If there is no SELinux policy rule that specifically allows access, such as for a process opening a file, access is denied. By default in CentOS 7, SELinux is enabled and in enforcing mode. Check the SELinux Status. Where to find SELinux permission denial details Now that you are aware that SELinux governs file access by verifying the security context of the process (the domain ) and the context of the file, it is time to find out how, if SELinux denies a certain access, you can troubleshoot this in more detail. Use the /usr/sbin/getenforce or /usr/sbin/sestatus commands to check the status of SELinux. The getenforce command returns Disabled if SELinux is disabled.
In this post, i will share on how to check Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) status on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 (RHEL 6). SELinux is a Linux feature that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies in the Linux kernel. First method to check the SELinux status is using sestatus command. The sestatus command returns the SELinux status and the SELinux policy being used on Linux RHEL 6 server as per below example:1.
How To Check Selinux Status In Redhat Linux 7
Simply run this command to check the SELinux status on your RHEL 6: root@rhel6 # /usr/sbin/sestatusSELinux status: disabledor root@rhel6 # sestatusSELinux status: disabled2. Alternatively, you can run this command: root@rhel6 # cat /etc/selinux/config# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.SELINUX=disabled# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values:# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,# mls - Multi Level Security protection.SELINUXTYPE=targetedIn above /etc/selinux/config, SELINUX is set to SELINUX=disabled.
Check If Selinux Is Running
If enable, it will be like below: root@rhel6 # cat /etc/selinux/config# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.SELINUX=permissive# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values:# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,# mls - Multi Level Security protection.SELINUXTYPE=targetedIf SELinux is enabled, it will look like SELINUX=permissive Categories, Tags,.